前言
最近有点时间,就想把网盘中收藏的一个大型项目实现一下,项目中涉及到图片的上传和下载,使用的是分布式文件系统FastDFS。而FastDFS图片服务器需要和Nginx整合后才能提供基于 HTTP协议的下载等功能,所以搭建FastDFS之前得需要简单的了解一下Nginx,于是就有了这篇Blog,后期会继续深入学习Nginx,所以这篇博客就简单的介绍一下Nginx及其安装过程。
一、Nginx 初识
1.1 什么是Nginx
Nginx 是一款高性能的 http 服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器。 由俄罗斯的程序设计师 Igor Sysoev 所开发,官方测试 nginx 能够支支撑 5 万并发链接,并 且 cpu、内存等资源消耗却非常低,运行非常稳定。
1.2 应用场景
- http 服务器。Nginx 是一个 http 服务可以独立提供 http 服务。可以做网页静态服务器。
- 虚拟主机。可以实现在一台服务器虚拟出多个网站。例如个人网站使用的虚拟主机。
- 反向代理,负载均衡。当网站的访问量达到一定程度后,单台服务器不能满足用户的请 求时,需要用多台服务器集群可以使用 nginx 做反向代理。并且多台服务器可以平均分担负载,不会因为某台服务器负载高宕机而某台服务器闲置的情况。
1.3 Nginx 安装
1.3.1 Windows环境的安装
- 下载 nginx:官方网站
- 将zip文件加压到自定义目录下即可。
- 加压文件后的主要目录说明:
- conf目录:存放Nginx的主要配置文件,很多功能实现都是通过配置该目录下的nginx.conf文件
- docs目录:存放Nginx服务器的主要文档资料,包括Nginx服务器的LICENSE、OpenSSL的LICENSE、PCRE的LICENSE以及zlib的LICENSE,还包括本版本的Nginx服务器升级的版本变更说明,以及README文档。
- html目录:存放了两个后缀名为.html的静态网页文件,这两个文件与Nginx服务器的运行相关
- logs目录:存放Nginx服务器运行的日志文件
- nginx.exe:启动Nginx服务器的exe文件,如果conf目录下的nginx.conf文件配置正确的话,通过该文件即可启动Nginx服务器
- 启动运行
- 双击加压后的文件中的nginx.exe文件,出现一闪而过的画面,则启动成功
- 然后在浏览器中输入 http://localhost或者 http://localhost:80 会出现启动成功的画面
1.3.2 Linux环境的安装
-
安装环境要求
-
需要安装 gcc 的环境
$ yum install gcc-c++ -
第三方的开发包
-
PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions) 是一个 Perl 库,包括 perl 兼容的正则表达式 库。nginx 的 http 模块使用 pcre 来解析正则表达式,所以需要在 linux 上安装 pc re 库。
$ yum install -y pcre pcre-devel -
zlib 库提供了很多种压缩和解压缩的方式,nginx 使用 zlib 对 http 包的内容进行 gzip, 所以需要在 linux 上安装 zlib 库。
$ yum install -y zlib zlib-devel -
OpenSSL是一个强大的安全套接字层密码库,囊括主要的密码算法、常用的密钥和证 书封装管理功能及 SSL 协议,并提供丰富的应用程序供测试或其它目的使用。 nginx 不仅支持 http 协议,还支持 https (即在 ssl 协议上传输 http),所以需要在 linux 安装 openssl 库。
$ yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
-
-
-
安装步骤
-
把 nginx 的源码包上传到 linux 系统
$ rz nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz -
安装编译
$ tar -zxvf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz $ cd nginx-1.8.0-
configure
# ./configure --help查询详细参数(参考本教程附录部分:nginx编译参数) # 进入 nginx 目录使用 configure 命令创建一 makeFile 文件。 # 参数设置如下: $ ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \ --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \ --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \ --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \ --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi注意:上边将临时文件目录指定为
/var/temp/nginx,需要在/var下创建temp及nginx目录$ mkdir /var/temp/nginx/client –p -
编译安装
$ make $ make install安装成功查看安装目录 :
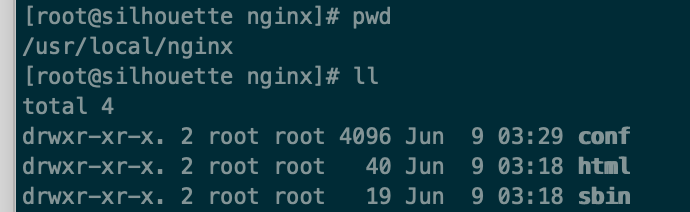
-
-
-
启动 Nginx
$ cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ $ ./nginx # 停止 nginx # 方式一:此方式相当于先查出nginx进程id再使用kill命令强制杀掉进程 $ ./nginx -s stop # 方式二:此方式停止步骤是待nginx进程处理任务完毕进行停止。 $ ./nginx -s quit # 重启 nginx # 方式一:先停止仔启动(建议使用) # 即:对nginx进行重启相当于先停止nginx再启动nginx,即先执行停止命令再执行启动命令。 $ ./nginx -s quit $ ./nginx # 方式二:重新加载配置文件 # 即:当nginx的配置文件nginx.conf修改后,要想让配置生效需要重启nginx,使用-s reload不用先停止nginx再启动nginx即可将配置信息在nginx中生效 $ ./nginx -s reload注意:执行
./nginx启动nginx,这里可以-c指定加载的nginx配置文件,如下:./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。如果不指定-c,nginx在启动时默认加载conf/nginx.conf文件,此文件的地址也可以在编译安装nginx时指定./configure的参数(--conf-path=**指向配置文件nginx.conf) -
访问 Nginx
nginx安装成功,启动nginx,即可访问虚拟机上的nginx;
192.168.30.201:80 -
开机自启动 nginx
-
编写 shell 脚本
$ vim /etc/init.d/nginx ## 脚本代码 #!/bin/bash # nginx Startup script for the Nginx HTTP Server # it is v.0.0.2 version. # chkconfig: - 85 15 # description: Nginx is a high-performance web and proxy server. # It has a lot of features, but it's not for everyone. # processname: nginx # pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid # config: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf nginxd=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx nginx_config=/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf nginx_pid=/var/run/nginx.pid RETVAL=0 prog="nginx" # Source function library. . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions # Source networking configuration. . /etc/sysconfig/network # Check that networking is up. [ ${NETWORKING} = "no" ] && exit 0 [ -x $nginxd ] || exit 0 # Start nginx daemons functions. start() { if [ -e $nginx_pid ];then echo "nginx already running...." exit 1 fi echo -n $"Starting $prog: " daemon $nginxd -c ${nginx_config} RETVAL=$? echo [ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/nginx return $RETVAL } # Stop nginx daemons functions. stop() { echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " killproc $nginxd RETVAL=$? echo [ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nginx /var/run/nginx.pid } # reload nginx service functions. reload() { echo -n $"Reloading $prog: " #kill -HUP `cat ${nginx_pid}` killproc $nginxd -HUP RETVAL=$? echo } # See how we were called. case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; reload) reload ;; restart) stop start ;; status) status $prog RETVAL=$? ;; *) echo $"Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|reload|status|help}" exit 1 esac exit $RETVAL -
设置文件的访问权限
# a+x ==> all user can execute 所有用户可执行 $ chmod a+x /etc/init.d/nginx $ /etc/init.d/nginx status|start|stop|restart -
加入到
rc.local文件中$ vim /etc/rc.local # 加入一行 /etc/init.d/nginx start 保存并退出,下次重启会生效。
-
1.4 配置虚拟主机
就是在一台服务器启动多个网站。如何区分不同的网站:域名不同、端口不同
1.4.1 通过端口区分不同虚拟机
Nginx 的配置文件: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
一个 server 节点就是一个虚拟主机,可以配置多个 server,配置了多个虚拟主机。
-
添加虚拟主机:
-
复制一份 html 文件夹
$ cp -r html html81 -
修改 html81 中的 index.html
-
修改 nginx 的配置文 nginx.conf 件如下:
worker_processes 1; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } } # 一个 server 节点就是一个虚拟主机 server { listen 81; server_name localhost; location / { root html81; index index.html index.htm; } } } -
重新加载配置文件
$ sbin/nginx -s reload
-
1.4.2 通过域名区分虚拟主机
-
域名就是网站。
www.baidu.com www.taobao.com www.jd.com -
Dns 服务器:把域名解析为 ip 地址。保存的就是域名和 ip 的映射关系。
# 一级域名: Baidu.com Taobao.com Jd.com # 二级域名: www.baidu.com Image.baidu.com Item.baidu.com # 三级域名: 1.Image.baidu.com Aaa.image.baidu.com一个域名对应一个 ip 地址,一个 ip 地址可以被多个域名绑定。
1.5 反向代理
1.5.1 反向代理
-
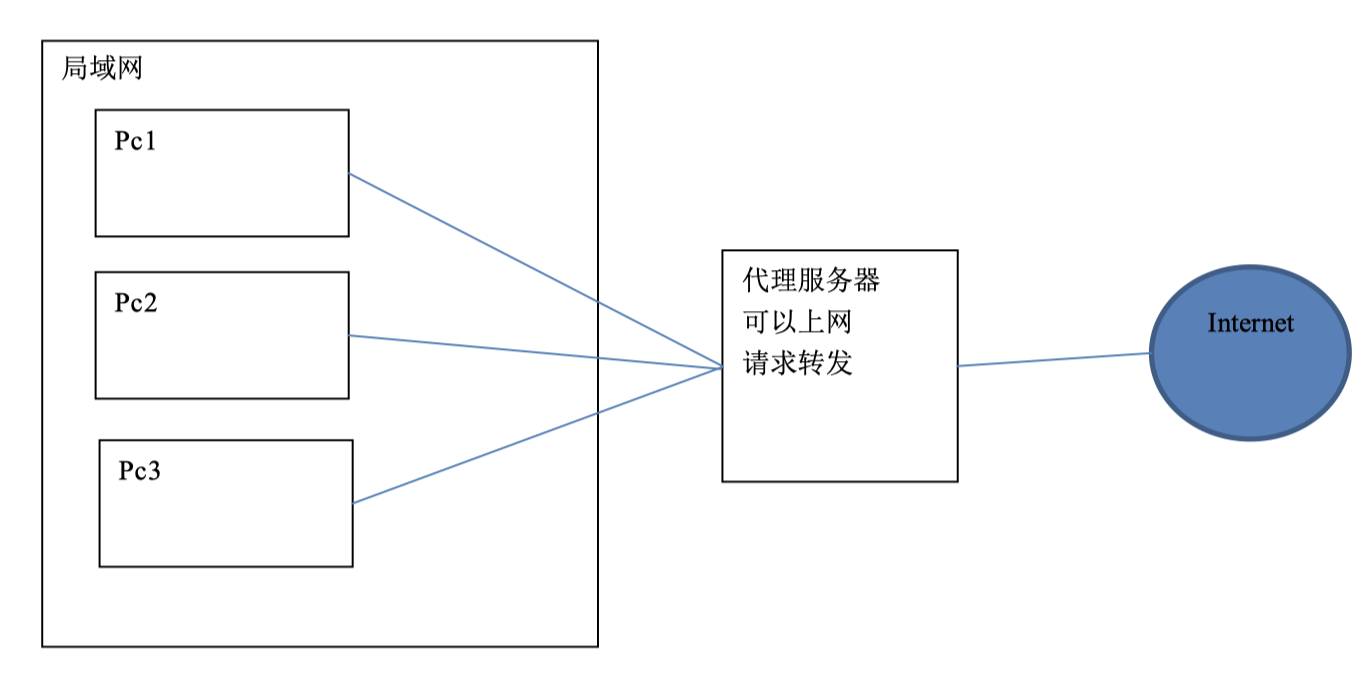
正向代理是在用户端。比如需要访问国外的网站,就需要VPN服务器将我们的IP地址变成国外的地址。
-
正向代理服务器位于客户端和服务器之间,为了向服务器获取数据,客户端要向代理服务器发送一个请求,并指定目标服务器,代理服务器将目标服务器返回的数据转交给客户端。这里客户端要进行一些正向代理的设置。
1.5.2 反向代理
-
反向代理,其实客户端对代理是无感知的,因为客户端不需要任何配置就可以访问,我们只需要将请求发送到反向代理服务器,由反向代理服务器去选择目标服务器获取数据后,在返回给客户端,此时反向代理服务器和目标服务器对外就是一个服务器,暴露的是代理服务器地址,隐藏了真实服务器IP地址。
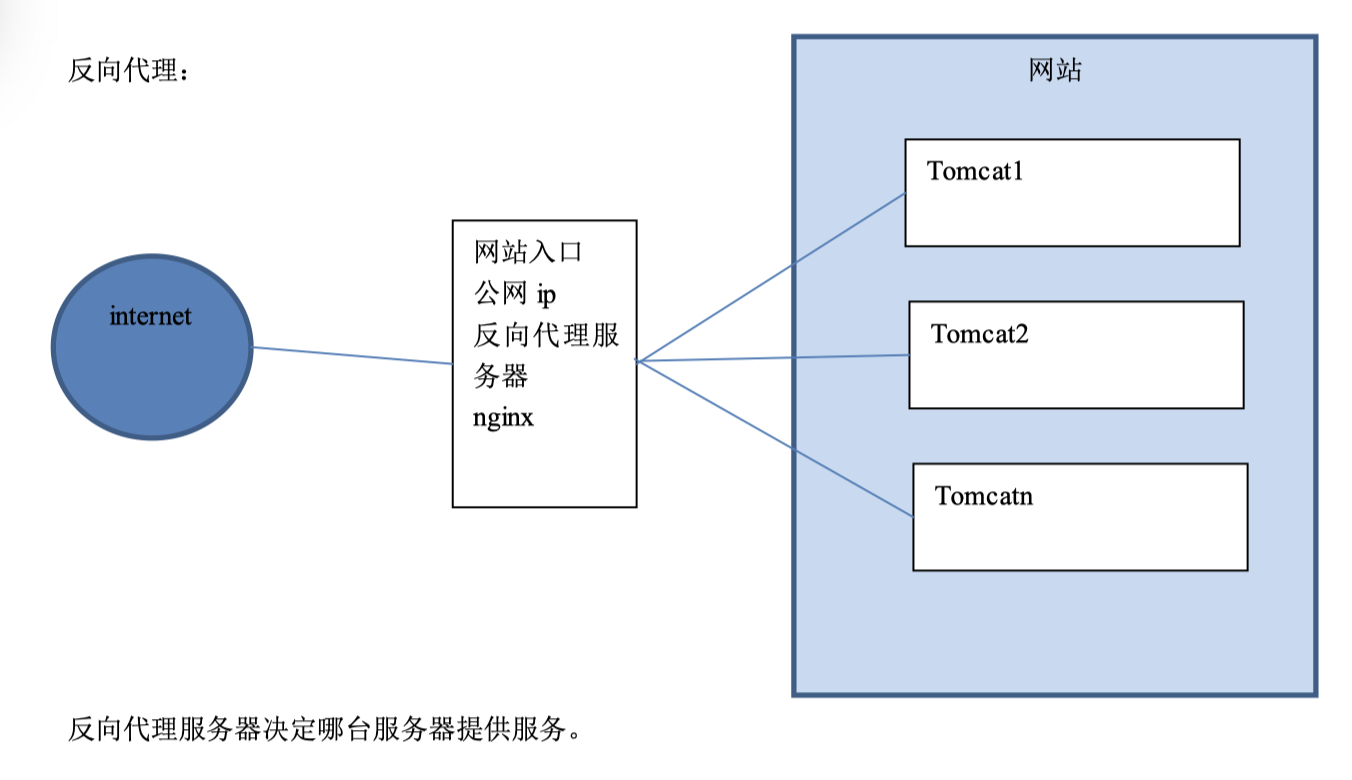
1.5.3 Nginx 实现反向代理
两个域名指向同一台 nginx 服务器,用户访问不同的域名显示不同的网页内容。 两个域名是 www.sian.com.cn 和 www.sohu.com
-
安装两个 tomcat,分别运行在 8080 和 8081 端口。
$ vim /home/silhouette/apache-tomcat-8.5.38-2/conf/server.xml注意:需要修改http访问端口(默认为8080端口)、监听tomcat关闭的端口(默认为8005)、负责接收其他http服务器的请求端口(默认为8009)。
-
修改两个tomcat的首页内容,启动两个 tomcat。
$ vim /home/silhouette/apache-tomcat-8.5.38-2/webapps/ROOT/index.jsp -
反向代理服务器的配置
upstream tomcat1{ server 192.168.30.77:8888; } server { listen 80; server_name 8888.silhouette.com; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcat1; index index.html index.htm; } } upstream tomcat2{ server 192.168.30.77:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name 8080.silhouette.com; location / { proxy_pass http://tomcat2; index index.html index.htm; } } -
nginx重新加载配置文件
$ ./nginx -s reload -
配置域名:在hosts文件中添加域名和ip的映射关系
$ vim /etc/hosts ####添加条目,如下: 192.168.30.77 8081.silhouette.com 192.168.30.77 8080.silhouette.com注意:配置域名与IP的映射是在宿主机上,而不是在虚拟机上