一、全文检索技术
1.1 数据分类
-
我们生活中的数据总体分为两种:结构化数据和非结构化数据。
-
结构化数据:指具有固定格式或有限长度的数据,如数据库,元数据等。
-
非结构化数据:指不定长或无固定格式的数据,如邮件,word文档等磁盘上的文件
-
1.2 数据的查询
-
结构化数据的查询
- SQL语句,查询结构化数据的方法。简单、速度快
-
非结构化数据的查询
- 顺序扫描法(Serial Scanning)
- 所谓顺序扫描,比如要找内容包含某一个字符串的文件,就是一个文档一个文档的看,对与每一个文档,从头看到尾,如果此文档包含此字符串,则此文档为我们要找的文件,接着看下一个文件,知道扫扫描完所有的文件。如利用 windows 的搜索也可以搜索文件内容,只是相当的慢。
- 全文检索(Full-text Search)
- 将非结构化数据中的一部分提取出来,重新组织,使其变得有一定结构,然后对此有一定结构的数据进行搜索,从而达到搜索相对较快的目的。这部分从非结构化数据中提取出的然后重新组织的信息,我们称之
索引。 - 这种先建立索引,再对索引进行搜索的过程称之为全文检索(Full-text Search)
- 虽然创建索引的过程也是比较耗时的,但是索引一单创建就可以多次使用,全文检索主要处理的是查询,所以耗时间创建索引是值得的。
- 将非结构化数据中的一部分提取出来,重新组织,使其变得有一定结构,然后对此有一定结构的数据进行搜索,从而达到搜索相对较快的目的。这部分从非结构化数据中提取出的然后重新组织的信息,我们称之
- 顺序扫描法(Serial Scanning)
-
搜索引擎的原理
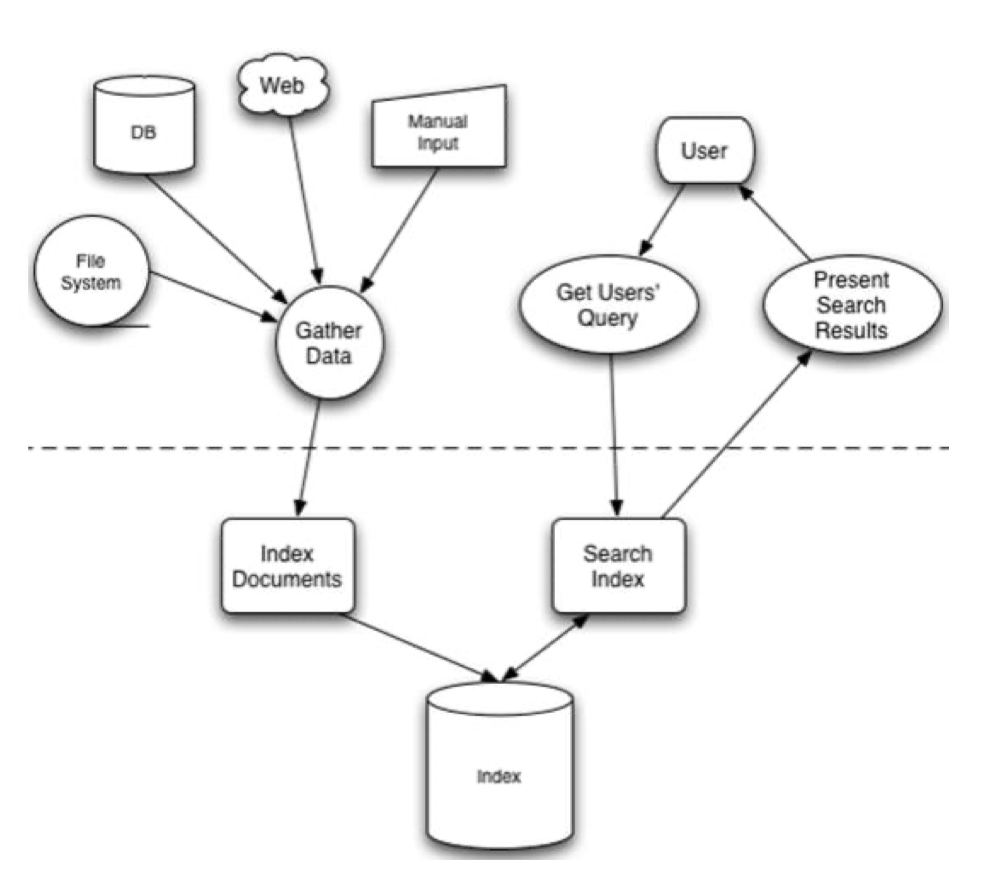
1.3 全文检索的实现和应用常见
- 实现
- 可以使用
Lucene实现全文检索。Lucene 是Apache 下的一个开放源码的全文引擎工具包。提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎。Lucene 的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以便在目标系统中实现全文检索的功能。 Lucene 是一个高性能、可伸缩的信息搜索(IR)库。它可以为你的应用程序添加索引和 搜索能力。Lucene 是用 java 实现的、成熟的开源项目,是著名的 Apache Jakarta 大家庭 的一员,并且基于 Apache 软件许可 [ASF, License]。同样,Lucene 是当前非常流行的、 免费的 Java 信息搜索(IR)库。
- 可以使用
- 应用场景
- 搜索引擎:百度、360检索、Google等搜索引擎
- 站内搜索:论坛搜索、微博、文章搜索
- 电商搜索:淘宝搜索、京东搜索
- 只要是有搜索的地方就可以使用全文检索技术。
- Lucene 与 Solr 的关系
- Lucene 是一套实现了全文检索的底层 API,提供对于全文检索的基础支持,而 Solr 是 全文检索引擎的一个实现产品,是一个企业级搜索应用服务器。
二、Lucene 实现全文检索的流程
2.1 索引和搜索流程图
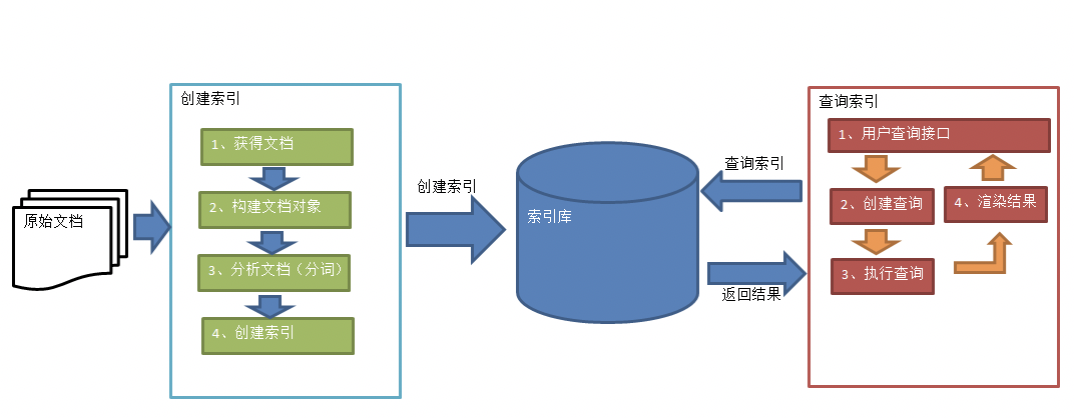
- 绿色表示创建索引过程,对要搜索的原始内容进行索引构建一个索引库,索引创建过程包括:确认原始内容即搜索的内容–>采集文档–>创建文档–>分析文档–>索引文档
- 红色表示搜索过程,从索引库中搜索内容,搜索过程包括:用户通过搜索界面–>创建查询–>执行搜索,从索引库搜索–>渲染搜索结果
2.2 创建索引
- 获取文档
- 原始文档:要基于那些数据来进行搜索,那么这些数据就是原始文档。
- 搜索引擎:使用爬虫技术获取原始文档
- 站内搜索:数据库中的数据
- 构建文档对象
- 对饮每个原始文档创建一个 Document 对象,每一个文档都有一个唯一的编号,就是文档ID
- 每个Document可以有多个Field(域),域中保存的就是原始数据。不同的Document可以有不同的Field,同一个Document可以有相同的Field。
- 域对象包含域的名称(Name)和域的值(value)
- 分析文档
- 将原始内容穿件为包含域(Field)的文档(Document),需要再对域中的内容进行分析,分析的过程是经过愿意文档提取单词、将字母转为小谢、去除标点符号、去除停用词等过程生成最终的语汇淡云,可以将语汇单元理解为一个一个的单词(管家词)。
- 每个单词叫做一个Term,不同的域中拆分出来的相同单词是不同的term。term中包含两部分:一部分是文档的域名,另一个是单词的内容。
- 创建索引
- 对所有文档分析得出的语汇单元进行索引,索引的目的是为了搜索,卒中要实现只搜索被索引的语汇单元从而找到Document(文档)。
- 创建索引是对语汇单元索引,通过词语着文档,这种索引的结构叫倒排索引结构
- 倒排索引结构也叫反向索引结构,包括索引和文档两部分,索引即词汇表,它的规模较小,而文档集合较大。
2.3 查询索引
- 用户插叙接口
- 全文检索系统提供用户搜索的界面供用户提交搜索的关键词,搜索完成展示搜索结果。
- 创建查询
- 用户输入查询关键字执行搜索之前需要见构建一个查询对象,查询对象中可以指定查询要搜索的 Field 文档域、查询关键字等,查询对象会生成具体的查询语法。
- 执行查询
- 根据查询语法在倒排索引词典表中找出对应搜索词的索引,从而找到索引所链接的文档链表。
- 渲染结果
- 以一个友好的界面将查询结果展示给用户,用户根据搜索结果找到自己想要的信息,为了帮助用户很快找到自己的结果,提供了很多展示的效果,比如搜索结果中将关键字高亮显示,百度提供的快照等。
三、Lucene的使用
3.1 配置开发环境
-
Lucene下载
- Lucene是开发全文检索功能的工具包,从官方网站下载压缩包,并解压。
- 此处下载的版本是lucene-7.4.0,JDK要求1.8以上。
-
使用的jar包
<dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.lucene/lucene-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId> <artifactId>lucene-core</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId> <artifactId>lucene-analyzers-common</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
3.2 创建索引
-
实现步骤
- 创建一个 Director 对象,指定索引库保存的位置
- 基于Directory对象创建一个IndexWriter对象
- 读取磁盘上的文件,对应每个文件创建一个文档对象
- 向文档对象中添加域
- 把文档对象写入索引库中
- 关闭indexWriter对象
-
代码实现
@Test public void createIndex() throws IOException { // 1. 创建一个 Director 对象,指定索引库保存的位置,可以是磁盘,也可以是内存 //Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();//保存到内存中(虽然速度快,但是占内存,用的比较少) //Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()); Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); //2. 基于Directory对象创建一个IndexWriter对象 IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(); IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,config); //3. 读取磁盘上的文件,对应每个文件创建一个文档对象 //File dir = new File("D:\\temp\\searchsource");//原始文档的路径 File dir = new File("/Users/silhouette/code/my-project/springsecurity/src/main/resources"); File[] files = dir.listFiles(); for (File file : files){ String fileName = file.getName(); //文件名 String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file);//文件内容 String filePath = file.getPath();//文件路径 long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file);//文件的大小 //创建文件名域Field (域的名称、域的内容、是否存储) Field fileNameField = new TextField("fileName",fileName,Field.Store.YES); Field fileContentField = new TextField("fileContent",fileContent,Field.Store.YES); Field filePathField = new TextField("filePath",filePath,Field.Store.YES); Field fileSizeField = new TextField("fileSize",String.valueOf(fileSize),Field.Store.YES); //4.创建document对象 Document document = new Document(); document.add(fileNameField); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileSizeField); //5.创建索引,并写入索引库 indexWriter.addDocument(document); } //6. 关闭indexWriter对象 indexWriter.close(); } -
使用 Luke 工具查看索引文件
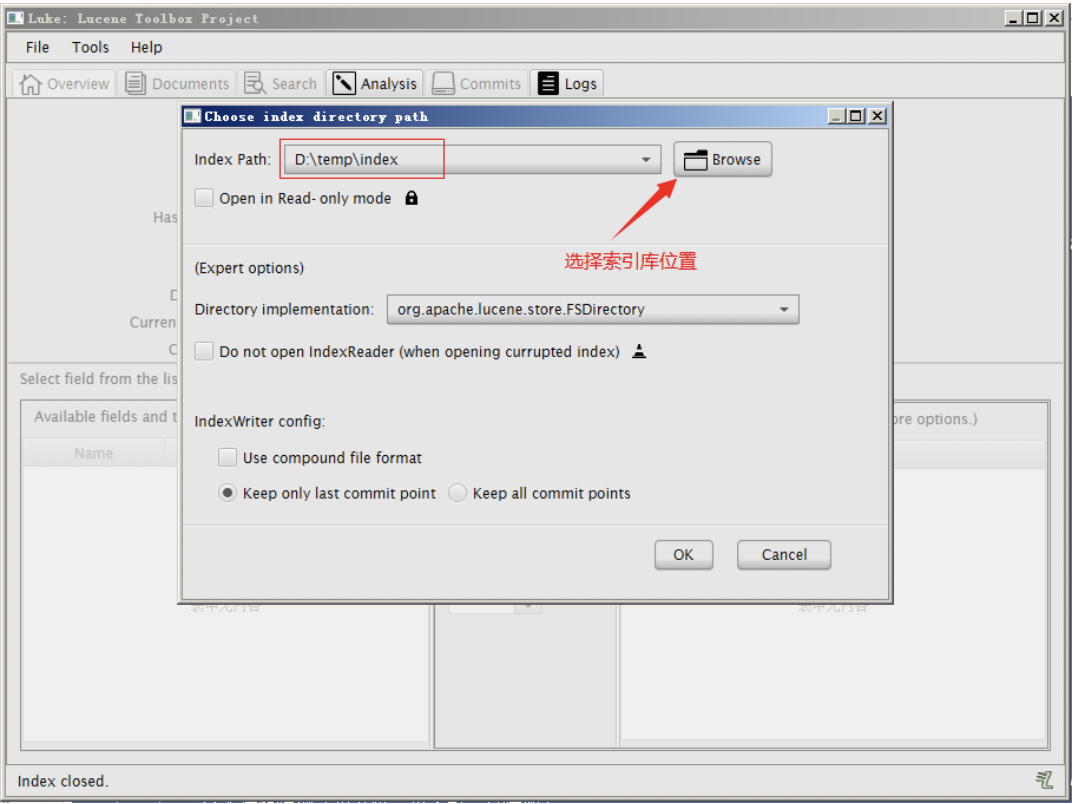
我们使用的luke的版本是luke-7.4.0,跟lucene的版本对应的。可以打开7.4.0版本的lucene创建的索引库。需要注意的是此版本的Luke是jdk9编译的,所以要想运行此工具还需要jdk9才可以。
3.3 查询索引
-
实现步骤
- 创建一个Directory对象,指向索引库的位置
- 创建一个IndexReader对象,需要指定Directory对象
- 创建一个IndexSearcher对象,需要指定IndexReader对象
- 创建一个TermQuery对象,需要指定查询的域和查询的关键字
- 执行查询,得到一个TopDocus对象
- 取查询结果的总记录数
- 取文档列表
- 打印文档中内容
- 关闭IndexReader对象
-
代码实现
@Test public void searchIndex() throws Exception { //1. 创建一个Directory对象,指向索引库的位置 //Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()); Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); //2. 创建一个IndexReader对象,需要指定Directory对象 IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); //3. 创建一个IndexSearcher对象,需要指定IndexReader对象 IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //4. 创建一个TermQuery对象,需要指定查询的域和查询的关键字 Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileContent","silhouette")); //5. 执行查询,得到一个TopDocus对象 //第一个参数是查询对象,第二个参数是查询结果返回的最大值 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query,10); //查询结果的总条数 System.out.println("查询结果的总条数:"+ topDocs.totalHits); //6. 取查询结果的总记录数 for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : topDocs.scoreDocs){ //scoreDoc.doc属性就是document对象的id //根据document的id找到document对象 Document document =indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println(document.get("fileName")); System.out.println(document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println(document.get("filePath")); System.out.println(document.get("fileSize")); System.out.println("-------------------------"); } //9. 关闭IndexReader对象 indexReader.close(); }
四、分析器
4.1 分析器的分词效果
查看IndexWriterConfig源码可知,默认使用的是标准分词器StandardAnalyzer。
-
查看分析器分分析效果
- 使用Analyzer对象的tokenStream方法返回一个TokenStream对象,词对象中包含了最终分词效果
-
实现步骤
-
创建一个Analyzer对象,StanderAnalyzer对象
-
使用分析器对象的tokenStream方法获得一个TokenStream对象
-
向TokenStream对象中设置一个引用,相当于一个指针
-
调用TokenStream对象中的rest方法,如果不调用抛异常
-
使用while循环遍历TokenStream对象
-
关闭TokenStream对象
-
-
代码实现
@Test public void testTokenStream() throws IOException { //1.创建一个Analyzer对象,StanderAnalyzer对象 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); //2.使用分析器对象的tokenStream方法获得一个TokenStream对象 //第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个,第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test","The Spring Framework provides"+ "a comprehensive programming and configuration model."); //TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("", // "查看IndexWriterConfig的源码可知,默认采用标准分析器进行分词解析"); //3.向TokenStream对象中设置一个引用,相当于一个指针 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); //添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); //4.调用TokenStream对象中的rest方法,如果不调用抛异常 //将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); //5.使用while循环遍历TokenStream对象 while(tokenStream.incrementToken()) { //关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); //取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); //结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } //6.关闭TokenStream对象 tokenStream.close(); }Tips:当分析英文时,会对单词进行解析;但是分析中文时,解析的竟然是一个字一个字的解析
4.2 中文分析器
-
StandardAnalyzer:就是按照中文一个字一个字地进行分词。
-
SmartChineseAnalyzer:对中文支持较好,但扩展性差,扩展词库,禁用词库和同义词库等不好处理
-
IKAnalyzer-
使用方法:
-
把jar包添加到工程中
-
把配置文件和扩展词典和停用词词典添加到classpath下
注意:hotword.dic和ext_stopword.dic文件的格式为UTF-8,注意是无BOM 的UTF-8 编码。也就是说禁止使用windows记事本编辑扩展词典文件
-
-
代码实现
@Test public void testIKAnalyzer() throws IOException { //创建一个Analyzer对象,StanderAnalyzer对象 Analyzer analyzer = new IKAnalyzer(); //使用分析器对象的tokenStream方法获得一个TokenStream对象 //第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个,第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("", "The Spring Framework “+ "陌生人 provides a comprehensive programming ."); //向TokenStream对象中设置一个引用,相当于一个指针 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); //将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); //5.使用while循环遍历TokenStream对象 while(tokenStream.incrementToken()) { //取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); } //关闭TokenStream对象 tokenStream.close(); }
Tips:运行上例会报错:“java.lang.AbstractMethodError: org.apache.lucene.analysis.Analyzer.createComponents(Ljava/lang/String;)Lorg/apache/lucene/analysis/Analyzer$TokenStreamComponents;”
-
出错分析:
- 查看IK分词器的源码pom.xml文件可知,IK分词器所依赖的lucene相关组件的版本为4.7.2,而示例使用的Lucene版本是7.4.0。两者版本不同,导致报错。
- 解决方法:从网上找了一个支持lucene 7.4.0的ik分词器的jar包,保持版本一致。然后将该jar包导入到项目中即可
-
使用IKAnalyzer分析器创建索引
@Test public void createIndex() throws IOException { // 1. 创建一个 Director 对象,指定索引库保存的位置,可以是磁盘,也可以是内存 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()); //2. 基于Directory对象创建一个IndexWriter对象 IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,config); //3. 读取磁盘上的文件,对应每个文件创建一个文档对象 File dir = new File("D:\\temp\\searchsource");//原始文档的路径 File[] files = dir.listFiles(); for (File file : files){ String fileName = file.getName(); //文件名 String fileContent = FileUtils.readFileToString(file);//文件内容 String filePath = file.getPath();//文件路径 long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file);//文件的大小 //创建文件名域Field (域的名称、域的内容、是否存储) Field fileNameField = new TextField("fileName",fileName,Field.Store.YES); Field fileContentField = new TextField("fileContent",fileContent,Field.Store.YES); Field filePathField = new TextField("filePath",filePath,Field.Store.YES); Field fileSizeField = new TextField("fileSize",String.valueOf(fileSize),Field.Store.YES); //4.创建document对象 Document document = new Document(); document.add(fileNameField); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileSizeField); //5.创建索引,并写入索引库 indexWriter.addDocument(document); } //6. 关闭indexWriter对象 indexWriter.close(); }
-
五、索引库的维护
5.1 添加索引库
-
Field域的属性
- 是否分析:是否对域的内容进行分分词处理。前提是我们要对域的内容进行查询
- 是否索引:将Field分析后的词或者整个Field进行索引,只有索引房可搜索到。
- 是否存储:将Field值存储都文档中,存储在文档中的Field才可以从Document中获取。
-
常见属性
Field类 数据类型 Analyzed 是否分析 Indexed 是否索引 Stored 是否存储 说明 StringField(FieldName, FieldValue,Store.YES)) 字符串 N Y Y或N 这个Field用来构建一个字符串Field,但是不会进行分析,会将整个串存储在索引中,比如(订单号,姓名等) 是否存储在文档中用Store.YES或Store.NO决定 LongPoint(String name, long… point) Long型 Y Y N 可以使用LongPoint、IntPoint等类型存储数值类型的数据。让数值类型可以进行索引。但是不能存储数据,如果想存储数据还需要使用StoredField。 StoredField(FieldName, FieldValue) 重载方法,支持多种类型 N N Y 这个Field用来构建不同类型Field 不分析,不索引,但要Field存储在文档中 TextField(FieldName, FieldValue, Store.NO) 或 TextField(FieldName, reader) 字符串 或 流 Y Y Y或N 如果是一个Reader, lucene猜测内容比较多,会采用Unstored的策略. -
添加文档代码实现
@Test public void addDocument() throws Exception { //索引库存放路径 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()); IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer()); //创建一个indexwriter对象 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config); //创建一个Document对象 Document document = new Document(); //向document对象中添加域。 //不同的document可以有不同的域,同一个document可以有相同的域。 document.add(new TextField("filename", "新添加的文档", Field.Store.YES)); document.add(new TextField("content", "新添加的文档的内容", Field.Store.NO)); //LongPoint创建索引 document.add(new LongPoint("size", 1000l)); //StoreField存储数据 document.add(new StoredField("size", 1000l)); //不需要创建索引的就使用StoreField存储 document.add(new StoredField("path", "d:/temp/1.txt")); //添加文档到索引库 indexWriter.addDocument(document); //关闭indexwriter indexWriter.close(); }
5.2 删除索引库
-
删除全部索引
@Test public void deleteAllIndex() throws Exception { IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(FSDirectory.open( new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()), new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer())); //删除全部索引 indexWriter.deleteAll(); //关闭indexwriter indexWriter.close(); }注意:将索引目录的索引信息全部删除,直接彻底删除,无法恢复。
-
指定查询条件删除
@Test public void deleteIndexByQuery() throws Exception { IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(FSDirectory.open( new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()), new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer())); //创建一个查询条件 Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("filename", "apache")); //根据查询条件删除 indexWriter.deleteDocuments(query); //关闭indexwriter indexWriter.close(); }
5.3 修改索引库
-
修改索引库的原理就是
先删除后添加@Test public void updateDocument() throws Exception { IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(FSDirectory.open( new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()), new IndexWriterConfig(new IKAnalyzer())); //创建一个新的文档对象 Document document = new Document(); //向文档对象中添加域 document.add(new TextField("name", "更新之后的文档", Field.Store.YES)); document.add(new TextField("name1", "更新之后的文档2", Field.Store.YES)); document.add(new TextField("name2", "更新之后的文档3", Field.Store.YES)); //更新操作 indexWriter.updateDocument(new Term("name", "spring"), document); //关闭索引库 indexWriter.close(); }
六、Lunece索引库查询
6.1 Lucene索引查询
对要搜索的信息创建Query查询对象,Lucene会根据Query查询对象生成最终的查询语法,类似关系数据库SQL语法一样 Lucene也有自己的查询语法,比如:“name:lucene”表示查询Field的name为“lucene”的文档对象。
可通过两种方法创建查询对象:
- 使用Lucene提供Query子类
TermQuery - 使用QueryParse解析查询表达式
6.2 TermQuery
-
TermQuery:根据关键字进行查询,需要指定要查询的域及腰查询的关键词
-
代码演示
@Test public void testTermQuery() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("D:\\temp\\index").toPath()); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建查询对象 Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("content", "lucene")); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); //共查询到的document个数 System.out.println("查询结果总数量:" + topDocs.totalHits); //遍历查询结果 for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : topDocs.scoreDocs) { Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName")); System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath")); System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize")); //System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } //关闭indexreader indexSearcher.getIndexReader().close(); }
6.3 WildcardQuery
-
WildcardQuery 可以进行测试通配符查询,
?可以代表任意一个字符,*可以任意多个任意字符。 -
代码演示
@Test public void testWildcardQuery() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); // 创建查询对象 Query query = new WildcardQuery(new Term("title", "*智能*")); // 搜索数据 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); // 获取总条数 System.out.println("本次搜索共找到" + topDocs.totalHits + "条数据"); //遍历查询结果 for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : topDocs.scoreDocs) { Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName")); System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath")); System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize")); //System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } //关闭indexreader indexSearcher.getIndexReader().close(); }
6.4 RangeQuery
-
RangeQuery:数值范围查询
-
NumericRangeQuery:根据数值范围查询(可以用来对非 String 类型的 ID 进行精确 的查找)
-
代码演示
@Test public void testRangeQuery() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建一个Query对象 Query query = LongPoint.newRangeQuery("size", 0l, 100l); //参数:域名、最小值、最大值、是否包含最小值、知否包含最大值 //Query query = NumericRangeQuery.newIntRange("size", 1, 2,true, true); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits); ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (ScoreDoc doc:scoreDocs){ Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName")); System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath")); System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize")); //System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } indexReader.close(); }
Tips:4.x.x版本时还可以使用NumericRangeQuery,但是我使用7.4.0版本时,发现找不到了,已被替换了,可以使用LongPoint.newRangeQuery()进行范围查询
6.5 QueryParser
-
QueryParser:可以对要查询的内容进行分词,然后基于分词的结果进行查询。
-
需要添加QueryParser依赖的Jar包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.lucene/lucene-queryparser --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.lucene</groupId> <artifactId>lucene-queryparser</artifactId> <version>7.4.0</version> </dependency>
-
-
代码演示
@Test public void testQueryParser() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建queryparser对象。第一个参数默认搜索的域,第二个参数就是分析器对象 QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser("content", new IKAnalyzer()); //使用QueryPaser对象创建一个Query对象 Query query = queryParser.parse("lucene是一个Java开发的全文检索工具包"); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits); ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (ScoreDoc doc:scoreDocs){ Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName")); System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath")); System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize")); //System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } indexReader.close(); }
6.6 组合查询
-
布尔查询本身没有查询条件,可以把其它查询通过逻辑运算进行组合, Occur.MUST 表示交集,Occur.SHOULD 表示并集,Occur.MUST_NOT 表示非。
-
代码演示
@Test public void testGroupQuery() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp").toPath()); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); // 创建查询对象 Query query1 = NumericRangeQuery.newIntRange("id", 1, 3,true, true); Query query2 = NumericRangeQuery.newIntRange("id", 2, 4,true, true); // 创建布尔查询的对象 BooleanQuery query = new BooleanQuery(); // 组合其它查询 query.add(query1, Occur.MUST_NOT); query.add(query2, Occur.SHOULD); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits); ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (ScoreDoc doc:scoreDocs){ Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc); System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName")); System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath")); System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize")); //System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent")); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } indexReader.close(); }
七、Lucene的高级使用
7.1 高亮显示
-
高亮显示的主要实现原理在于,为所有的关键字添加一个HTML标签,通过改标签来设置高亮。
-
代码演示
@Test public void testHighLighter() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp4")); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建queryparser对象。第一个参数默认搜索的域,第二个参数就是分析器对象 QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_47,"fileContent", new IKAnalyzer()); //使用QueryPaser对象创建一个Query对象 Query query = queryParser.parse("freemarker"); // 格式化器 Formatter formatter = new SimpleHTMLFormatter("<em>","</em>"); Scorer scorer = new QueryScorer(query); // 准备高亮工具 Highlighter highlighter = new Highlighter(formatter,scorer); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits); ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (ScoreDoc doc:scoreDocs){ //取文档id int docId = doc.doc; //根据id取文档对象 Document document = indexSearcher.doc(docId); // 处理查询结果 String fileContent = document.get("fileContent"); String result = highlighter.getBestFragment(new IKAnalyzer(), "fileContent", fileContent); System.out.println("result:" + result); System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线"); } indexReader.close(); }Tips:运行结果可知,所有的搜索关键字都被标签包裹起来了。注意,此次使用的Lucene的版本是
4.7.2,因为我在7.4.0未找到关于高亮的接口或实现类。
7.2 排序
@Test
public void testQuerySort() throws Exception {
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp7").toPath());
IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader);
//创建queryparser对象。第一个参数默认搜索的域,第二个参数就是分析器对象
QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser("fileContent", new IKAnalyzer());
//使用QueryPaser对象创建一个Query对象
Query query = queryParser.parse("freemarker");
// 创建排序对象,false升序,true降序
Sort sort = new Sort(new SortField("id", SortField.Type.INT, true));
//执行查询
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10,sort);
System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
for (ScoreDoc doc:scoreDocs){
//取文档id
int docId = doc.doc;
//根据id取文档对象
Document document = indexSearcher.doc(docId);
System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath"));
System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize"));
//System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent"));
System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线");
}
indexReader.close();
}
7.3 分页
@Test
public void testPageQuery() throws Exception{
//每页条数
int pageSize = 2;
//当前页码
int pageNum = 3;
//当前页的起始条数
int start = (pageNum - 1) * pageSize;
//当前页的结束条数
int end = start + pageSize;
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp7").toPath());
IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader);
//创建queryparser对象。第一个参数默认搜索的域,第二个参数就是分析器对象
QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser("fileContent", new IKAnalyzer());
//使用QueryPaser对象创建一个Query对象
Query query = queryParser.parse("freemarker");
// 创建排序对象,false升序,true降序
Sort sort = new Sort(new SortField("id", SortField.Type.INT, false));
//执行查询
TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, end,sort);
System.out.println("总记录数:" + topDocs.totalHits);
ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs;
//避免数据越界
if (end > scoreDocs.length){
end = scoreDocs.length;
}
for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
ScoreDoc scoreDoc = scoreDocs[i];
//获取文档对象
Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDoc.doc);
System.out.println("fileName:" + document.get("fileName"));
System.out.println("filePath:" + document.get("filePath"));
System.out.println("fileSize:" + document.get("fileSize"));
//System.out.println("fileContent:" + document.get("fileContent"));
System.out.println("-----------------华丽的的分割线");
}
indexReader.close();
}
7.4 加权算法
Lucene会对搜索结果进行打分,用来表示文档数据与词条关联性的强弱,得分越高,表示查询的匹配度就越高,排名就越靠前。
-
创建索引
@Test public void CreateWeightIndex() throws Exception { // 创建一个 Director 对象,指定索引库保存的位置,可以是磁盘,也可以是内存 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp4")); // 基于Directory对象创建一个IndexWriter对象 IndexWriterConfig indexWriterConfig = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_47,new IKAnalyzer()); IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory,indexWriterConfig); Document document = new Document(); Random random = new Random(); // 创建Filed需要制定字段的名称,字段的内容,还需要设置是否需要存储 IndexableField fieldId = new IntField("id", 10, Field.Store.YES); TextField fieldTitle = new TextField("title", "title " + 10, Field.Store.YES); //设置加权 fieldTitle.setBoost(2.0f); IndexableField fieldHits = new IntField("hits", random.nextInt(1000), Field.Store.YES); // 向document中添加字段 document.add(fieldTitle); document.add(fieldId); document.add(fieldHits); //添加文档 indexWriter.addDocument(document); //提交 indexWriter.commit(); indexWriter.close(); } -
查询索引
/** * 修改权重并重新创建索引,然后再进行查询索引查看效果 */ @Test public void QueryWeightIndex() throws Exception { Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("/Users/silhouette/Downloads/temp4")); IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建queryparser对象。第一个参数默认搜索的域,第二个参数就是分析器对象 QueryParser queryParser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_47,"title", new IKAnalyzer()); //使用QueryPaser对象创建一个Query对象 Query query = queryParser.parse("title"); TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 20); ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (int i = 0 ; i < scoreDocs.length ; i++) { Document document = indexSearcher.doc(scoreDocs[i].doc); String id = document.get("id"); String title = document.get("title"); String hits = document.get("hits"); System.out.println(id + ":" + title+":"+hits); } indexReader.close(); }
Tips:此示例使用的Lucene版本是是
4.7.2,在7.4.0上未找到加权的相应方法